algebra_with_sympy
Algebraic Equations with SymPy
Introduction | Output Formatting | Installation | Try Live | Issues or Comments | Change Log | License | GIT Repository | PyPi Link
Website/Documentation (including API)
Introduction
This tool defines relations that all high school and college students would
recognize as mathematical equations.
They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by
the relation operator "=". In addition, it sets some convenient defaults and
provides some controls of output formatting that may be useful even if
you do not use the Equation class (see Conveniences for
SymPy).
This tool applies operations to both sides of the equation simultaneously, just
as students are taught to do when
attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement Equation/b
yields a new equation Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b
The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange equations and perform algebra in a stepwise fashion using as close to standard mathematical notation as possible. In this way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling over missed details such as a negative sign.
A simple example as it would appear in a Jupyter notebook is shown immediately below:
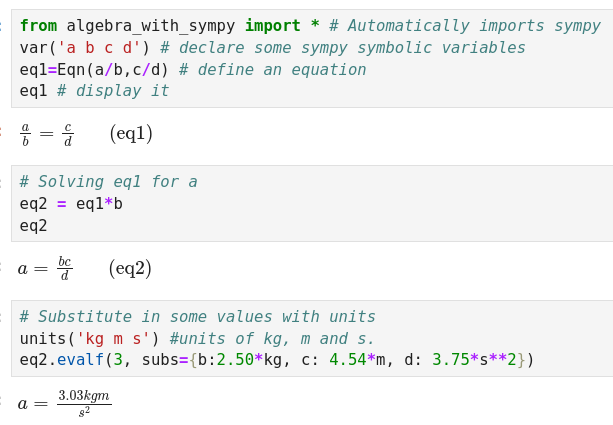
The last cell illustrates how it is possible to substitute numbers with
units into the solved equation to calculate a numerical solution with
proper units. The units(...) operation is part this package, not Sympy.
In IPython environments (IPython, Jupyter, Google Colab, etc...) there is
also a shorthand syntax for entering equations provided through the IPython
preparser. An equation can be specified as eq1 =@ a/b = c/d.
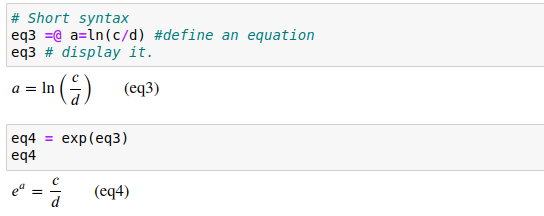
If no Python name is
specified for the equation (no eq_name to the left of =@), the equation
will still be defined, but will not be easily accessible for further
computation. The =@ symbol combination was chosen to avoid conflicts with
reserved python symbols while minimizing impacts on syntax highlighting
and autoformatting.
More examples of the capabilities of Algebra with Sympy are here.
Many math packages such as SageMath and Maxima have similar capabilities, but require more knowledge of command syntax, plus they cannot easily be installed in a generic python environment.
Convenience Tools and Defaults for Interactive Use of SymPy
Even if you do not use the Equation class, there are some convenience
tools and defaults that will probably make interactive use of SymPy in
Jupyter/IPython environments easier:
- By default, all numbers in Sympy expressions without decimal points are
interpreted as integers (e.g.
2/3*x, where x is a sympy symbol, ->2*x/3notx*0.6666..., but if x is just a plain Python object then2/3*x->x*0.66666...). This can be turned off withunset_integers_as_exact(), which leads to standard Python behavior (2/3*x->x*0.6666...) even for Sympy expressions. Turn on withset_integers_as_exact(). When on the flagalgwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True. - Results of
solve()are wrapped inFiniteSet()to force pretty-printing of all of a solution set. See Controlling the Format of Interactive Outputs. - It is possible to set the default display to show both the pretty-printed result and the code version simultaneously. See Controlling the Format of Interactive Outputs.
Controlling the Format of Interactive Outputs
- These controls impact all Sympy objects and the
Equationclass. - In graphical environments (Jupyter) you will get rendered Latex such as
$\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$ or $e^{\frac{-x^2}{\sigma^2}}$. To also see the
code representation (what can be copied and pasted for
additional computation) set
algwsym_config.output.show_code = True. This will print the code version (e.g.Equation(a,b/c)) of equations and sympy expression in addition to the human readable version. This code version can be accessed directly by callingrepr()on the equation or expression.
In interactive text environments (IPython and command line) The human readable string version of Sympy expressions are returned (for
Equationsa = b rather than Equation(a,b)). This is equivalent to Callingprint()orstr()on an expression.- To have the code version (can be copied and pasted as a
Python statement) returned, set
algwsym_config.output.human_text = False. - Setting both
algwsym_config.output.human_text = Trueandalgwsym_config.output.show_code = True, will return both the code and human readable versions.
- To have the code version (can be copied and pasted as a
Python statement) returned, set
The equation label can be turned off by setting
algwsym_config.output.label = False.Automatic wrapping of
Equationsas Latex equations can be activated by settingalgwsym_config.output.latex_as_equationstoTrue. The default isFalse. Setting this toTruewraps output as LaTex equations, wrapping them in\begin{equation}...\end{equation}. Equations formatted this way will not be labeled with the internal name for the equation, independent of the setting ofalgwsym_config.output.label.By default solutions output by
solve()are returned as a SymPyFiniteSet()to force typesetting of the included solutions. To get Python lists instead you can override this for the whole session by settingalgwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True. For a one-off, simply wrap the output of a solve inlist()(e.g.list(solve(...))). One advantage of list mode is that lists can be ordered. Whenalgwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = Truesolve()maintains the solutions in the order the solve for variables were input.
Setup/Installation
- Use pip to install in your python environment:
pip install -U Algebra-with-SymPy - To use in a running python session issue
the following command :
from algebra_with_sympy import *. This will also import the SymPy tools. - If you want to isolate this tool from the global namespace you are
working with change the import statement
to
import algebra_with_sympy as spa, wherespastands for "SymPy Algebra". Then all calls would be made tospa.funcname(). WARNING: Doing this makes shorthand equation input and control of interactive output formats unavailable. To recover this functionality the following code must be run in the interactive session.
Equation = spa.Equation
Eqn = Equation
algwsym_config = spa.algwsym_config
Try in binder
Issues or Comments
- Issues and bug reports should be filed on github.
- Comments, questions, show and tell, etc. should go in the project discussions.
Change Log
- 1.1.3 (September 7, 2025)
- Better checking for an incompatible sympy installation and improved warning on how to solve the problem.
- Shifting to more modern
pyproject.tomlpackaging. - Updates to Developer documentation to reflect packaging changes.
- Moved determination of equation (actually any sympy basic object) python name to this package from the equation object, thus simplifying what is included in sympy.
- Minor test updates.
- Added overrides of __repr__ and __str__ in preparation for inclusion of Equation class in Sympy.
- 1.1.2 (August 13, 2024)
- Test updates.
- Verified compatibility with Sympy 1.13.2.
- 1.1.1 (July 25, 2024)
- BUG FIX accommodate empty re.search results in preparser. Prevents unnecessary error messages.
- 1.1.0 (July 22, 2024)
- Setting integers as exact (
set_integers_as_exact(), the default) now only sets integers as exact within Sympy and Algebra_with_Sympy expressions. This increases compatibility with other packages that depend on integers being Python integers. - Refuse to import Algebra_with_Sympy if an incompatible version of Sympy is installed in the environment.
- Added warning explaining how to install a compatible version of Sympy.
- Setting integers as exact (
- 1.0.2 (July 5, 2024)
- Removed requirements for Jupyter and Jupyterlab as code will work in vanilla python or Google Colab.
- Workaround for Google Colab's inconsistent handling of mixed Latex and plain text strings. This impacted display of equation labels in Colab.
- BUG FIX: catch IPython not installed so that can run in plain vanilla python.
- 1.0.1 (May 22, 2024)
- BUG FIX: equation labels that include underscore characters "_" are now accepted.
- BUG FIX: wrapping equations formatted as LaTex equation (ie. surrounded
by
\begin{equation}...\end{equation}) in the$..$code used to indicate markdown for MathJax was causing output errors in Quarto when outputing to .tex or .pdf. This is now fixed without negatively impacting MathJax rendering. - BUG FIX: Singleton results of solve unnecessarily wrapped by extra list or finiteset. No longer double nested.
- BUG FIX: When returning lists make solve respect user order of solutions.
- BUG FIX: Equation output threw error when Algebra_with_Sympy was imported as a submodule. Equation labeling turned off for this type of import to avoid error.
- BUG FIX: Equation labels are now copyable even with the newer MathJax commonHTML rendering.
- Updates to requirements.txt.
- Documentation updates.
- 1.0.0 (January 2, 2024)
- Added convenience operation
units(...)which takes a string of space separated symbols to use as units. This simply declares the symbols to be positive, making them behave as units. This does not create units that know about conversions, prefixes or systems of units. This lack is on purpose to provide units that require the user to worry about conversions (ideal in a teaching situation). To get units with built-in conversions seesympy.physics.units. - Fixed issue #23 where
cos()multiplied by a factor was not the same type of object aftersimplify()acted on an expression. Required embedding theEquationtype in the sympy library. UntilEquationis incorporated into the primary Sympy repository a customized version of the latest stable release will be used. - Fixed issue where trailing comments (ie.
# a commentat the end of a line) lead to input errors using compact=@notation. algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equationshas a default value ofFalse. Setting this toTruewraps output as LaTex equations wrapping them in\begin{equation}...\end{equation}. Equations formatted this way will not be labeled with the internal name for the equation.
- Added convenience operation
- 0.12.0 (July 12, 2023)
- Now defaults to interpreting numbers without decimal points as integers.
This can be turned off with
unset_integers_as_exact()and on withset_integers_as_exact(). When on the flagalgwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True.
- Now defaults to interpreting numbers without decimal points as integers.
This can be turned off with
- 0.11.0 (June 5, 2023)
- Formatting of
FiniteSetsoverridden so that the contents always pretty-print. This removes the necessity of special flags to get pretty output fromsolve. - Sympy
solve()now works reliably with equations and outputs pretty-printed solutions. - Added option
algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = Truewhich causessolve()to return solutions sets as Python lists. Using this option prevents pretty-printing of the solutions produced bysolve(). algwsym_config.output.show_codeandalgwsym_config.output.human_textnow work for all sympy objects, not justEquationobjects. This works in terminal, IPython terminal and Jupyter. This is achieved by hooking into the pythondisplay_hookand IPythondisplay_formatter.- Added jupyter to requirements.txt so that virtual environment builds will include jupyter.
- The way
__version__was handled could break pip install. Changed to generating the internal version during setup. This means the version is now available asalgwsym_version.
- Formatting of
- 0.10.0 (Sep. 5, 2022)
- Documentation updates and fixes.
- Significantly increased test coverage (~98%).
- Support for
Eqn.rewrite(Add) - Solving (e.g.
solve(Eqn,x)) now supported fully. Still experimental. - Bug fix: latex printing now supports custom printer.
- Substitution into an Equation using Equations is now
supported (e.g.
eq1.subs(eq2, eq3, ...)). algebra_with_sympy.__version__is now available for version checking within python.- Bug fix: preparsing for
=@syntax no longer blocksobj?syntax for getting docstrings in ipython. - More robust determination of equation names for labeling.
- 0.9.4 (Aug. 11, 2022)
- Update to deal with new Sympy function
piecewise_exclusivein v1.11. - Added user warning if a function does not extend for use with
Equationsas expected. This also allows the package to be used even when a function extension does fail. - Simplification of documentation preparation.
- Typo fixes in preparser error messages.
- Update to deal with new Sympy function
- 0.9.3 (Aug. 9, 2022)
- Added check for new enough version of IPython to use the preparser.
- If IPython version too old, issue warning and do not accept
=@shorthand.
- 0.9.2 (Jun. 5, 2022)
=@shorthand syntax for defining equations in IPython compatible environments.- Fixed bug where
root()override calledsqrt()on bare expressions.
- 0.9.1 (Mar. 24, 2022)
- Equations labeled with their python name, if they have one.
- Added flags to adjust human readable output and equation labeling.
- Accept equation as function argument in any position.
- First pass at
solve()accepting equations. - Added override of
root()to avoid warning messages. - More unit tests.
- First pass at documentation.
- 0.9.0 functionality equivalent to extension of SymPy in PR#21333.
licensed under GNU V3 license
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
Copyright - Algebra with Sympy Contributors 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024
Development Notes
General | Make Docs | Running Tests | Build PyPi Package|
General Notes
- TODOs
- Test collect when there isn't an available _eval_collect (not sure how to get there).
- Test for _binary_op NotImplemented error (not sure how to get there).
- To consider
- Include Sympy Plot Backends in the default setup.
- Change
Equationconstructor to acceptEquality,Set,Listorlhs, rhs, rather than justlhs, rhs. - Extend
.substo accept.subs(a=2*c, b = sin(q), ...). - MathLive on another web page as possible input engine.
Constructing the Documentation
- Make sure pdoc is installed and updated in the virtual environment
pip install -U pdoc. - Update any
.mdfiles included in_init_.py.- Generally URLs should be absolute, not relative.
- At the root level run pdoc
pdoc --logo https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/alg_w_sympy.svg --logo-link https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/ --footer-text "Algebra with Sympy vX.X.X" --math -html -o docs ./algebra_with_sympywhereX.X.Xis the version number.
Tasks for Documentation
- Readme.md & Development Notes.md
- Use absolute path to github pages for more examples.
Running Tests
- Install updated pytest in the virtual environment:
pipenv shell
pip install -U pytest
- Run standard tests:
pytest --ignore='Developer Testing' --ignore-glob='*test_preparser.py'. - Run preparser tests:
ipython -m pytest tests/test_preparser.py - Run doctests:
pytest --ignore='tests' --ignore='Developer Testing' --ignore-glob='*old*' --doctest-modules
You can run all the tests using the dotests script: ./dotests.sh.
NOTE: Some warnings about invalid escape characters are expected because raw strings are being passed with specialized LaTex escaped characters.
Building PyPi package
- Make sure to update the version number in setup.py first.
- Install updated setuptools and twine in the virtual environment:
pipenv shell
pip install -U setuptools wheel twine
- Build the distribution
python -m build. Test it on
test.pypi.org.- Upload it (you will need an account on test.pypi.org):
python -m twine upload --repository testpypi dist/*. Create a new virtual environment and test install into it:
exit # to get out of the current environment cd <somewhere> mkdir <new virtual environment> cd <new directory> pipenv shell #creates the new environment and enters it. pip install -i https://test.pypi.org/..... # copy actual link from the # repository on test.pypi.There are often install issues because sometimes only older versions of some of the required packages are available on test.pypi.org. If this is the only problem change the version to end in
rc0for release candidate and try it on the regular pypi.org as described below for releasing on PyPi.- After install test by running a jupyter notebook in the virtual environment.
- Upload it (you will need an account on test.pypi.org):
Releasing on PyPi
Proceed only if testing of the build is successful.
- Double check the version number in
algebra_with_sympy/version.py. - Rebuild the release:
python -m build. - Upload it:
python -m twine upload dist/* - Make sure it works by installing it in a clean virtual environment. This
is the same as on test.pypi.org except without
-i https://test.pypy.... If it does not work, pull the release.
1""" 2.. include:: ../ReadMe.md 3.. include:: ../Development Notes.md 4""" 5__docformat__ = "numpy" 6from warnings import warn 7proper_sympy = True 8try: 9 from sympy import Equation 10except ImportError: 11 proper_sympy = False 12 warn('You need the extended version of Sympy to use Algebra_with_Sympy. ' 13 'Algebra_with_Sympy will not be loaded. You can use your current ' 14 'version of Sympy without the Algebra_with_Sympy features using ' 15 'the command `from sympy import *`. To get the extended version ' 16 'of sympy:\n' 17 '1. Uninstall your current version `pip uninstall sympy`.\n' 18 '2. If sympy-for-algebra is also installed, it must be uninstalled.\n' 19 ' `pip uninstall sympy-for-algebra`.\n' 20 '3. (Re)install extended sympy `pip install sympy-for-algebra`.\n' 21 'NOTE: an update to extended sympy is usually issued soon after ' 22 'each 1.XX.1 release of standard sympy.') 23 24if proper_sympy: 25 from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import * 26 27 # Set up numerics behaviors 28 try: 29 from IPython import get_ipython 30 31 if get_ipython(): 32 get_ipython().input_transformers_post.append(integers_as_exact) 33 algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True 34 except ModuleNotFoundError: 35 pass 36 37 from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import * 38 39 # Set the output formatting defaults 40 algwsym_config.output.show_code = False 41 algwsym_config.output.human_text = True 42 algwsym_config.output.label = True 43 algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = False 44 algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations = False 45 46 # Set version number for internal access 47 algwsym_version = 'unknown' 48 try: 49 from algebra_with_sympy.version import __version__ as algwsym_version 50 except FileNotFoundError as e: 51 UserWarning('Could not read the version.py file. Your installation' 52 ' of algebra_with_sympy probably did not work correctly.')